Want to know the difference between Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics?
Here it is:
Google Tag Manager is a Tag Management System that lets you add analytics tools tracking snippets without touching any code. In contrast, Google Analytics is an analytics tool that collects and displays website data in fancy charts and graphs.
But that’s only the basics.
In this article, we’ll take a look at more of the differences between these free tools provided by Google.
We’ll also look at the benefits of using these tools together and how to set them up.
Let’s dive in.
What is Google Analytics?
Google Analytics is a free tool by Google that shows you information about your website traffic.
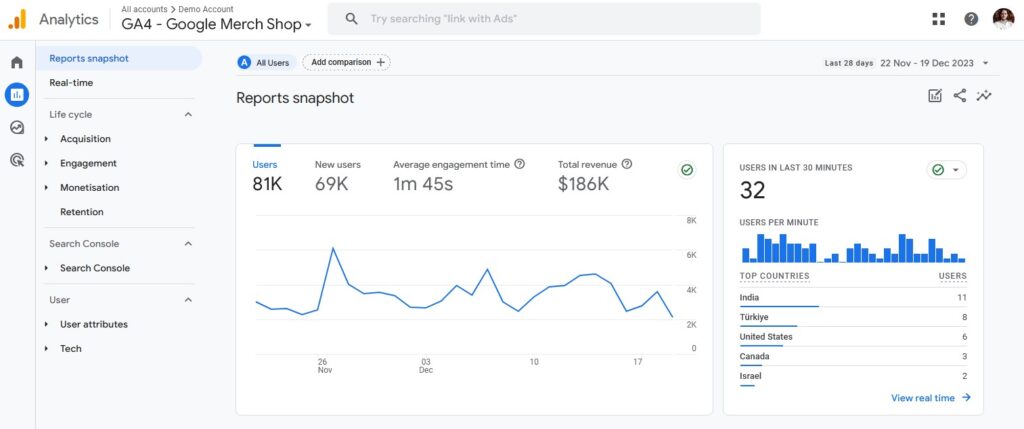
It collects all kinds of data about your website’s visitors and presents them in visually appealing graphs, tables, and reports.
You can track things like visitor count, amount of time spent on a page, traffic sources, conversions, and much more.
Google Analytics has been the most widely used web analytics tool since 2019, thanks to its accessibility and free price tag.
What is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager is another free tool by Google that allows you to add tracking tags to your website without the need to modify code.
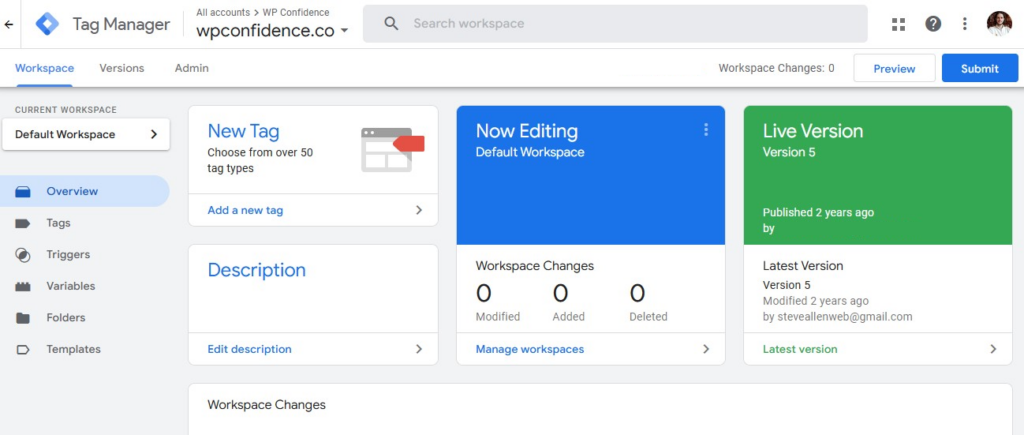
Tracking or marketing tags are little snippets of code that collect data and monitor user behavior.
The initial setup involves adding a Tag Manager snippet to your site. More on this later.
Once this snippet has been added, you’re able to add tracking codes from a variety of analytics software from a user-friendly interface.
Tracking software commonly used with Google Tag Manager includes Google Analytics, Meta Pixel, Google Ads, and CRO tools.
Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics: What’s the Difference?
The main difference between Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics is that GA tracks and displays website metrics, whereas GTM deploys and manages tracking codes.
Google Analytics is one of the tracking codes (tags) that can be managed by Google Tag Manager.
However, both tools can be used independently from one another or used together to collect more granular metrics.
Both tools are free and require a steep learning curve to master advanced configurations, but that’s where the similarities end.
Here’s a deeper dive into the differences between Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics.
1. Purpose and Functionality
The purpose and functionality of Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics are very different.
Google Analytics’ main purpose is to track and analyze website traffic and user behavior.
For example, it collects data about how your website is performing, such as page views, traffic sources, user demographics, conversion data, and more. Then, it presents this valuable information visually using graphs, charts, and tables.
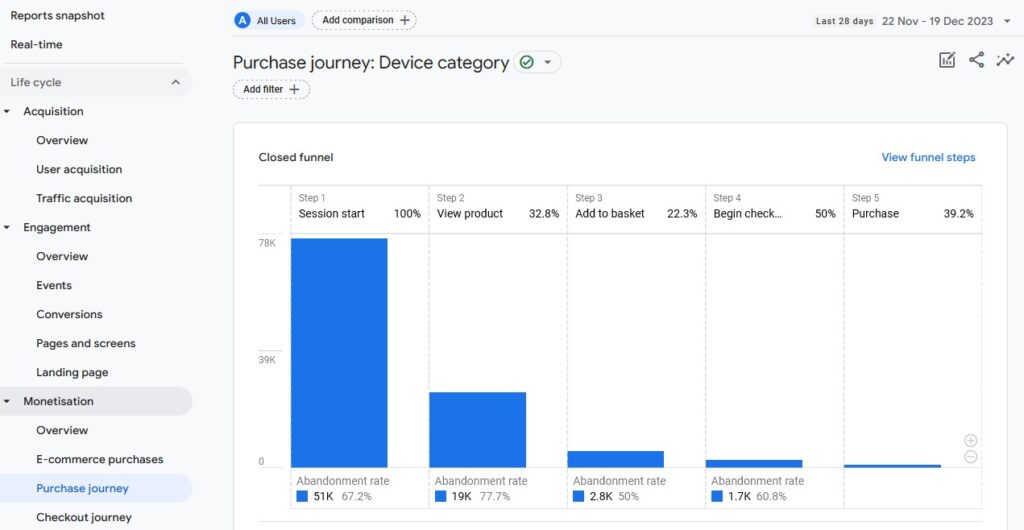
This helps you make better decisions around content, user experience, and optimizing conversions.
Google Tag Manager, on the other hand, doesn’t collect data per se. Instead, it’s used primarily to add and manage tracking codes in a centralized user interface.
The tracking codes, also known as Tags or Pixels, are added to the tool from external analytics tools, such as Google Analytics.
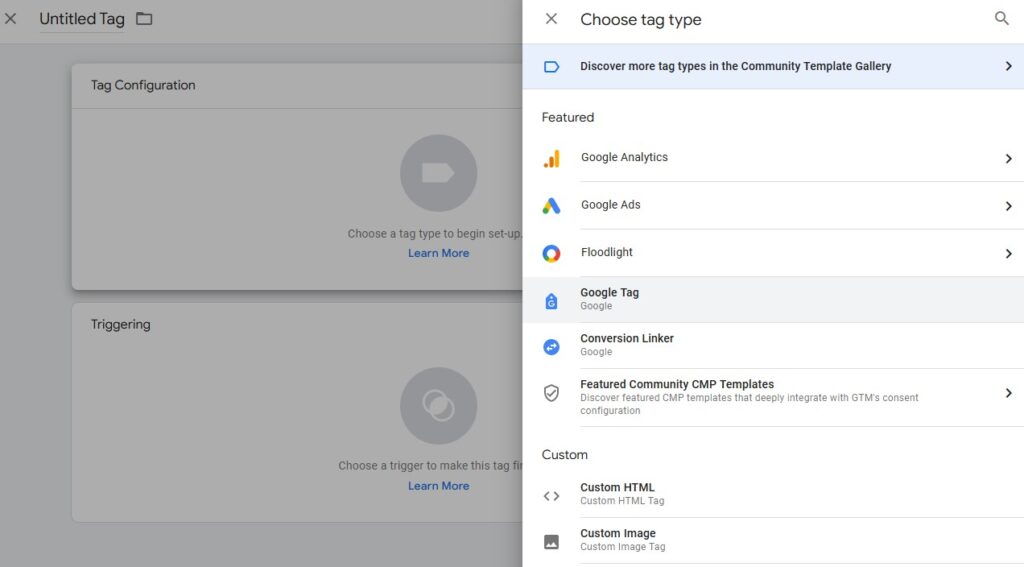
That means you only need to add the GTM code once. Tracking software codes is then added to Tag Manager’s web interface instead of needing to fiddle with code or requiring a developer.
2. Reporting Capabilities
When it comes to reporting, this is where Google Analytics shines. It provides various dashboards full of different types of reports in a visually appealing way. These include graphs, colorful charts, and interactive tables.
On the flip side, Google Tag Manager doesn’t offer any kind of reporting at all. Instead, it works in the background, communicating to Google Analytics about the type of data it needs to collect.
3. Tag Management
To install Google Analytics on your website, you need to add a snippet of code to the head of every page. If you’re using a CMS like WordPress, this isn’t too much of an issue, but if your site is static, it can be challenging to get working effectively across your entire website.
This is especially the case if you need to track intricate metrics on different pages, as you’ll need to make custom configurations to the tracking code.
This is where Google Tag Manager shines, as it facilitates tag management dynamically. That means you’re able to adjust how the tag collects data and on which pages, without needing to edit the source code of your site manually.
4. User Interface and Complexity
More differences between Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager crop up when comparing the interfaces of both tools.
Ever since the sunsetting of Universal Analytics, marketers and business owners have struggled to come to terms with the new Google Analytics 4 layout.
You can access basic data about your website’s traffic performance relatively easily, but when it comes to diving into more sophisticated reporting, the tool can become complicated to use.
With Google Tag Manager, things are a little more streamlined and intuitive. Sure, the tools are intended for different purposes, and often used in conjunction with each other, but Tag Manager has the upper hand in user experience.
5. Dependency
Google Analytics, by itself, is a standalone tool capable of collecting all the data you need about your website visitors. Allbeit, requiring a steep learning curve to implement advanced engagement metrics.
However, Google Tag Manager requires Google Analytics (or a third-party analytics tool) to collect specific data points, as it doesn’t collect data itself; it only deploys tags that do the work.
6. Event Tracking
Another difference between Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics is how events are triggered.
When it comes to Google Analytics, basic event tracking comes as standard with the code snippet. You can also enable Enhanced Measurements, which tracks extras such as scroll tracking, outbound clicks, internal site search, form interactions, video engagements, and more.
More tailored configurations, however, aren’t as straightforward as clicking some buttons, as you’ll need to write custom code and add it to the HTML of your site.
In contrast, Google Tag Manager simplifies the process of adding event tracking with the use of triggers. These detect specific interactions on your site on specified pages through its intuitive interface without needing to touch a line of code.
7. Access and Control
Unless you’re a developer, making adjustments to Google Analytics code will require help from one. This can add unexpected costs to your marketing budget or prevent you from seeing the right data if it isn’t set up correctly.
Google Tag Manager is a little more forgiving when it comes to learning how things work. Even though GTM will take some getting used to, there are a ton of tutorials on YouTube that can help you implement more intricate tracking without understanding the code.
That’s great news for marketers and non-developers who need more flexibility and control when managing the way Google Analytics collects data.
Benefits of Using GTM and GA4 Together
Now you know what the differences are between Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics; you might be wondering why does it matter?
Well, when used in combination with each other, they offer several benefits that optimize the data collected, streamline marketing tag management, and help you understand how visitors behave on your website or mobile app.
Here are some of the most notable benefits:
- Simplified tag implementation and centralized tracking: GTM allows you to add and manage tracking tags for GA and other analytics tools, saving you time and not needing to rely on developers to do it for you.
- Ease of event tracking: GTM lets you set up event tracking for specific user interactions, such as button clicks and form submissions, without needing to write custom tags.
- Enhanced data layer control: GTM uses a data layer to temporarily store data before sending it to GA, providing more accurate data collection.
- Testing and debugging: The built-in debugging tool in GTM allows tags to be tested and verified they are working properly before making them live. This can prevent errors from occurring and skewing reporting data.
- Faster deployment of changes: GTM lets you make changes to your tracking setup quickly, without needing to wait for website code updates. This is particularly helpful in fast-paced marketing environments.
- Improved performance: GTM loads tags asynchronous, meaning they load in the background, improving website performance and page load times.
- Version control and rollback: GTM saves all changes made to tags in the form of versions. If anything breaks, you can roll back to a previous version and try again.
By harnessing the strengths of both Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics, you get the best of both worlds.
A powerful analytics setup and tag management software that provides more streamlined and intricate configurations.
How to Setup GTM with Google Analytics – Step-by-Step
By now, you may have seen the benefits of using Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics together and want to know how to set them up.
Whether you’re already using Google Analytics and want to migrate to Google Tag Manager or are brand new to both, the following steps will guide you through the process.
Let’s get started.
Step 1: Create a Google Analytics Account and Property
If you already have a GA4 account and property, you can skip this step.
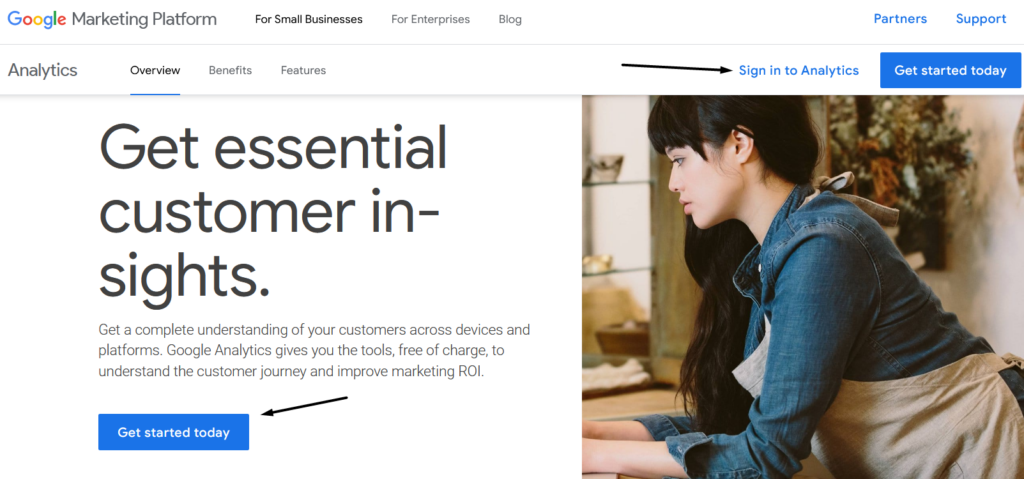
Go to the Google Analytics website and click Get Started Today:
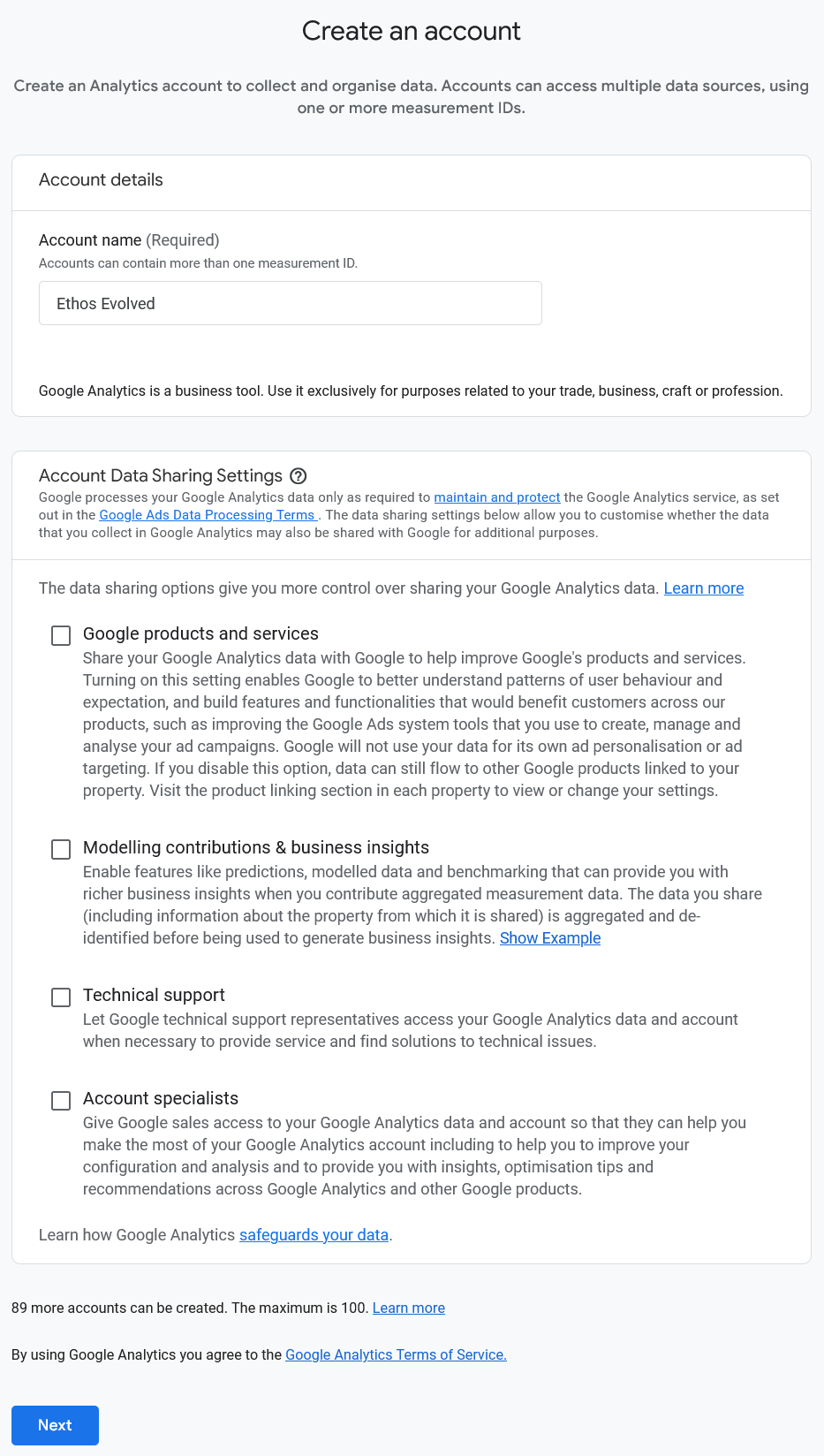
Next, fill in the account details and click Next:
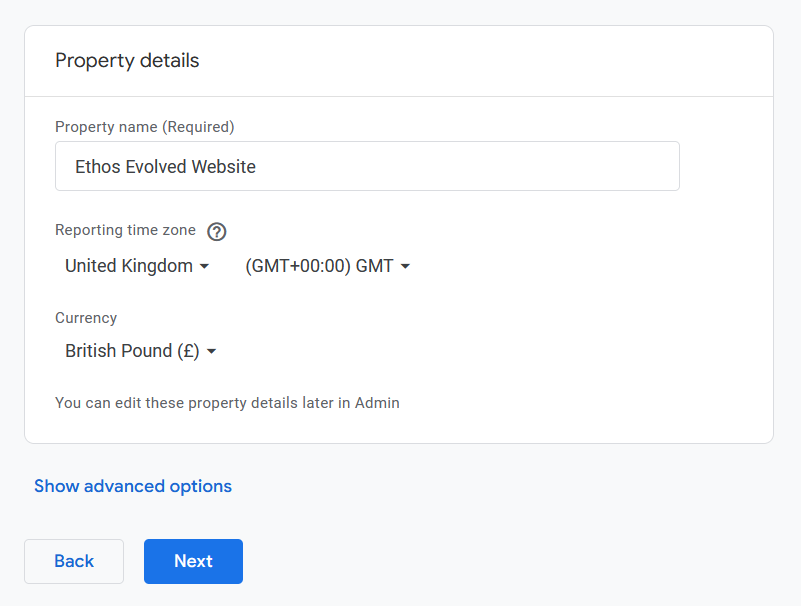
Then fill in your Property name, and reporting time zone and click Next:
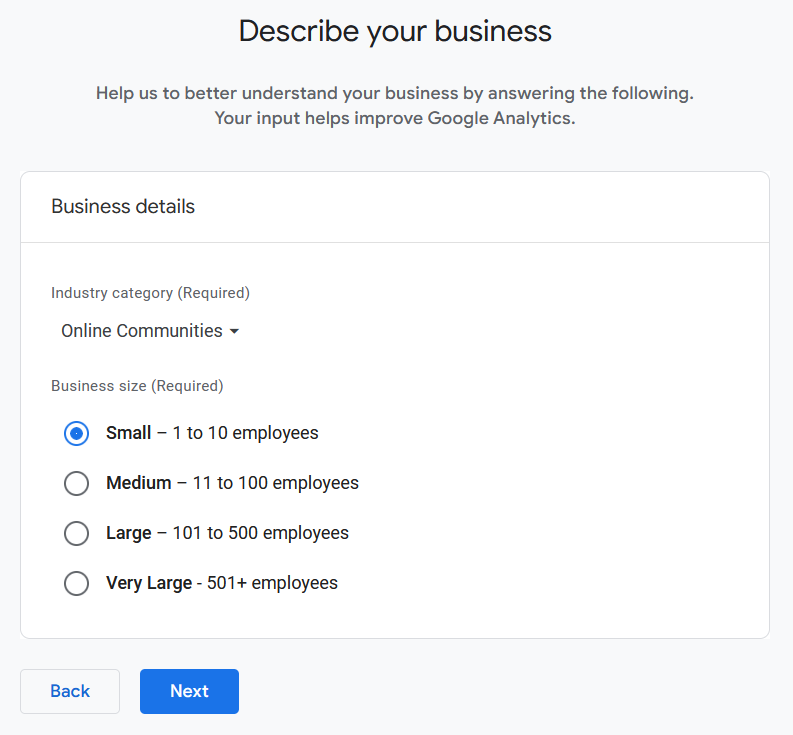
Choose your Industry category and Business size, then click Next:
Then click on Web:
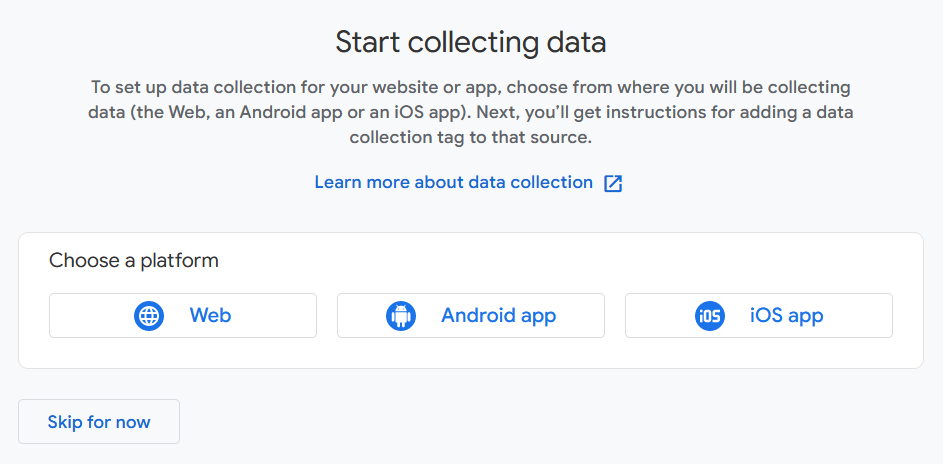
Add your Website URL and Stream name, then click Create stream:
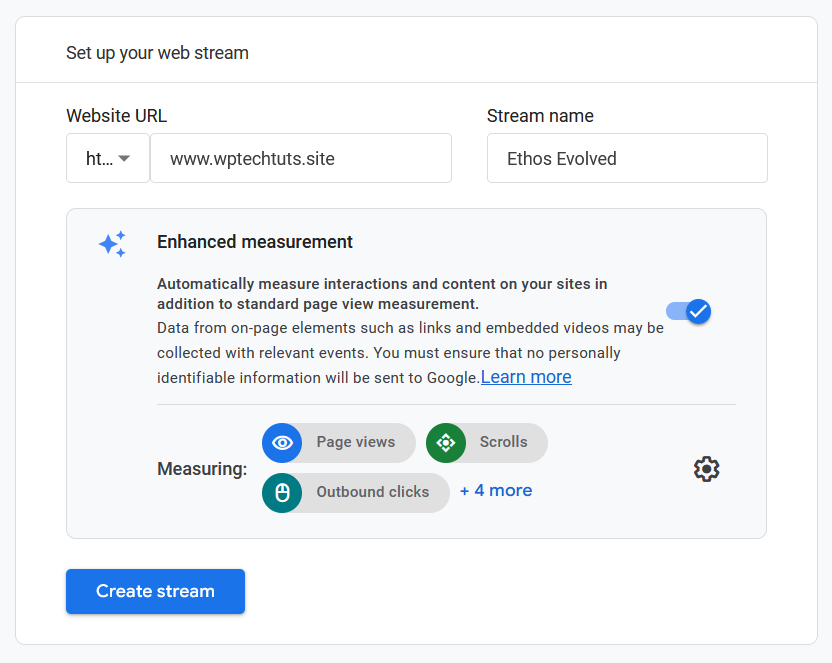
That’s it. The next step is to create a Google Tag Manager account.
Step 2: Create a Google Tag Manager Account
Go to Google Tag Manager and click on Start for free:
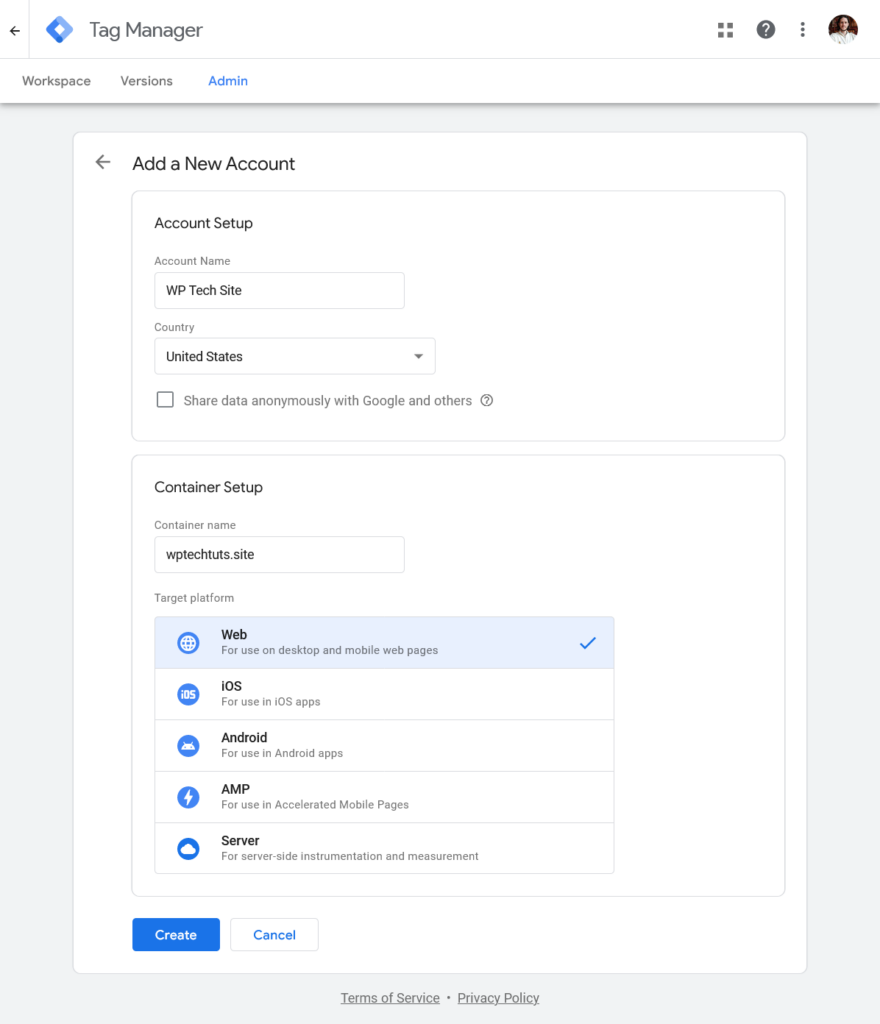
Create a new account and enter your details about your website or app:
Step 3: Add the Google Tag Snippet to Your Website
If you’re setting up GTM and GA4 with your website, you’ll see this code in a popup window:
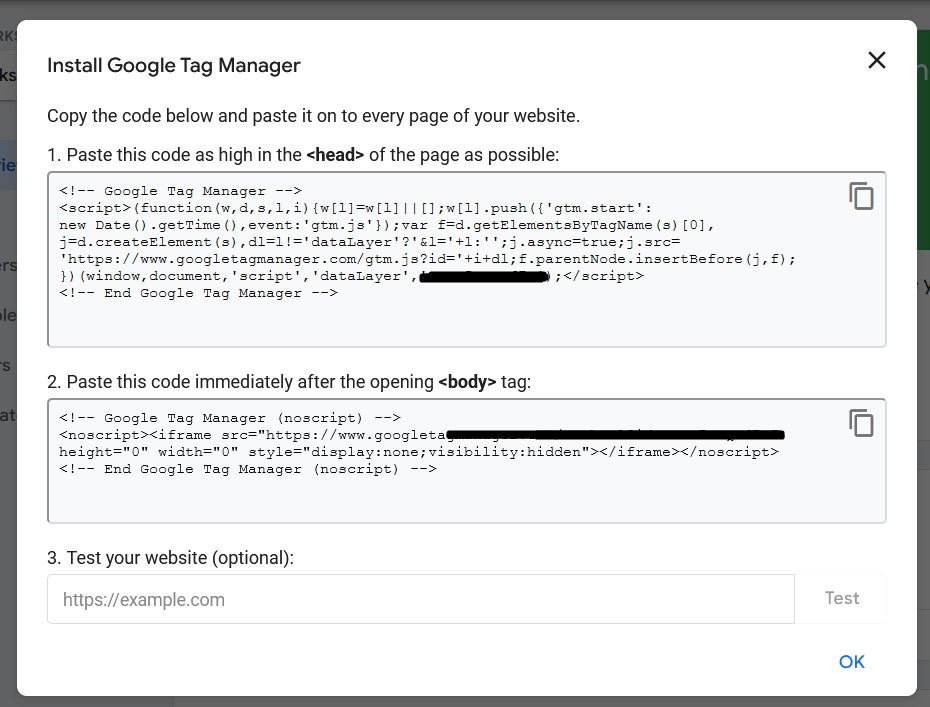
You need to paste the top code in between the <head></head> tags of your website’s HTML.
You might need to get a developer to help you with this, but if you’re using WordPress, you can access the file in your WordPress dashboard.
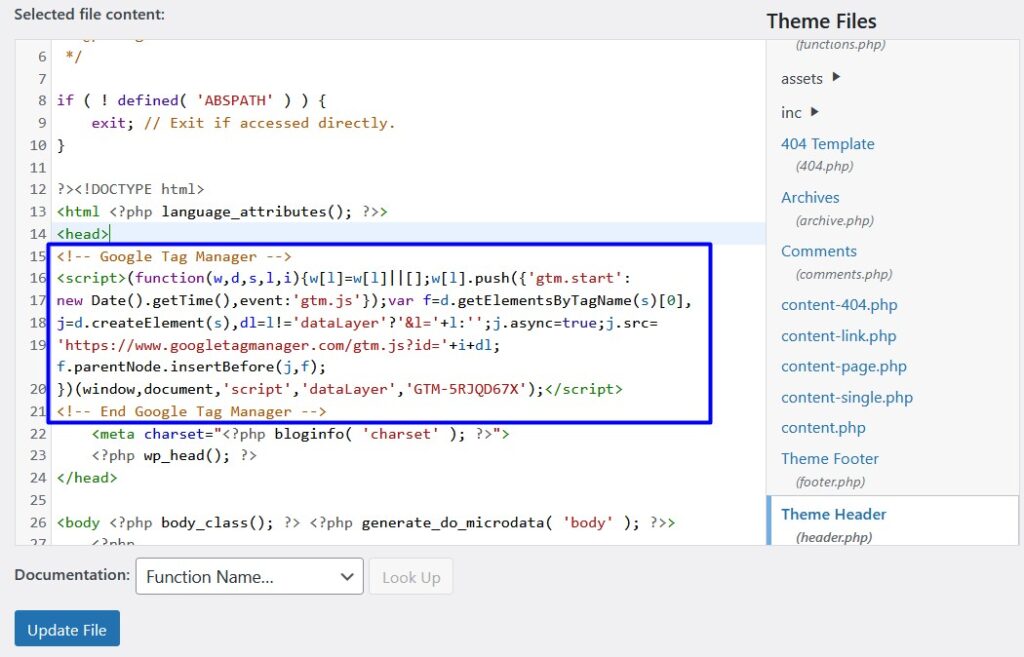
Navigate to Appearance > File Editor and click on header.php. Make sure you’re editing a child theme file and not the main theme; otherwise, the snippet will be overwritten when the theme updates.
Here is where to paste the top snippet, right below the <head> tag:
Then copy the bottom snippet and paste it below the <body> tag:
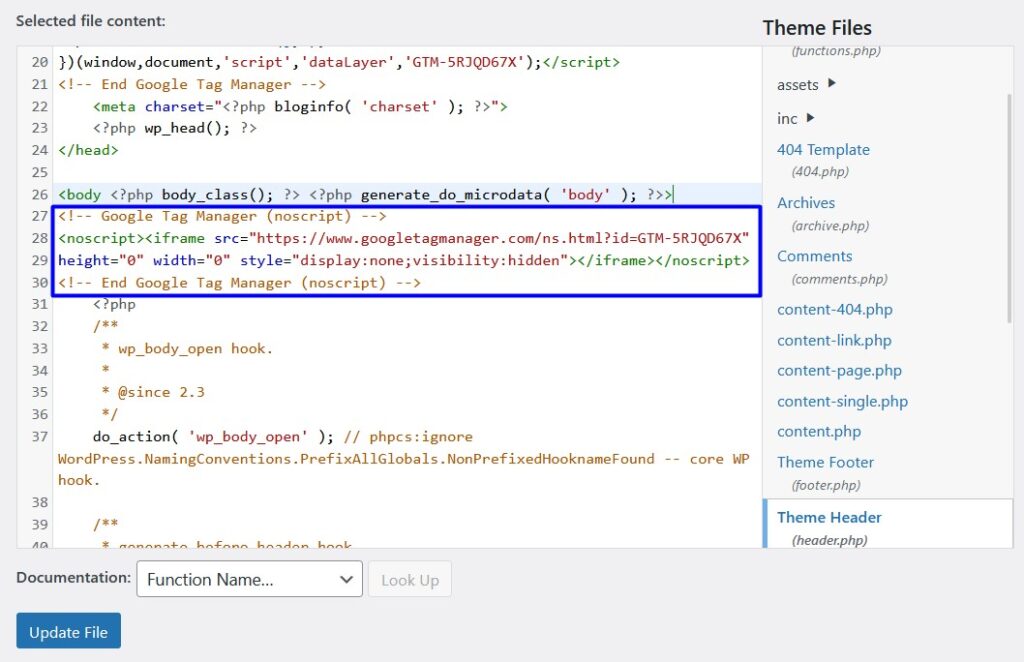
Update the file and then go back to Google Tag Manager.
You can test to see if the Tag is active on your site by clicking the Preview button. This will open up a popup box where you add your domain name.
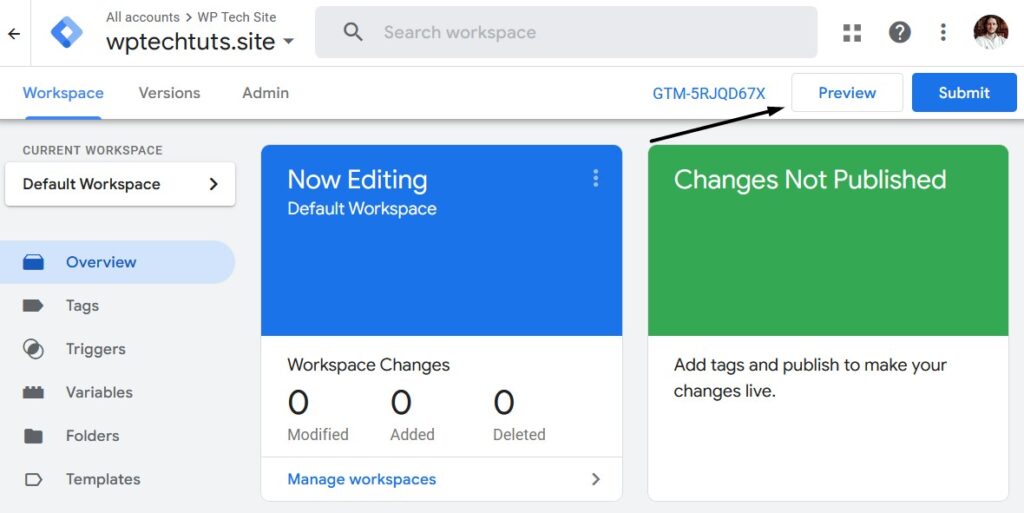
If everything is working, you’ll see a popup box that looks like this:
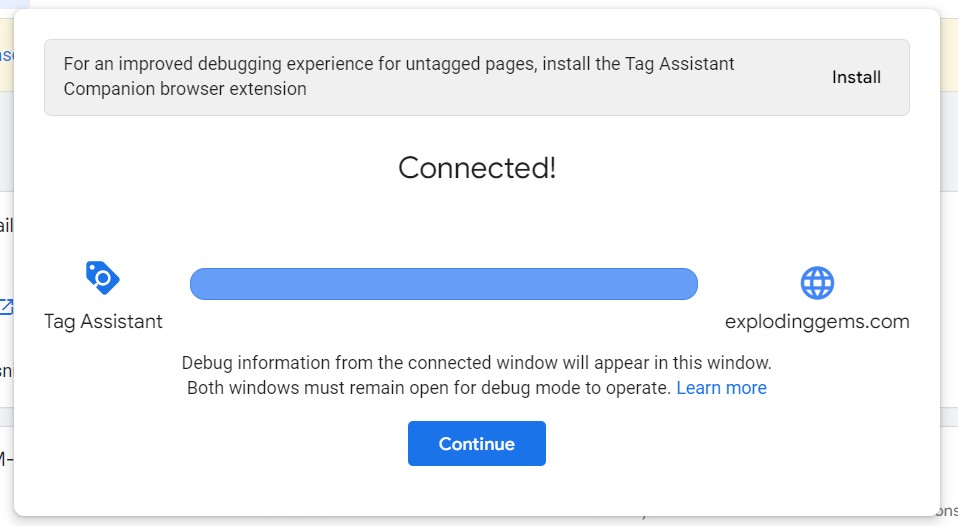
Step 4: Add your GA4 Tracking ID to GTM
Now it’s time to add the Measurement ID from Google Analytics to Tag Manager. You’ll find this in your web data stream:
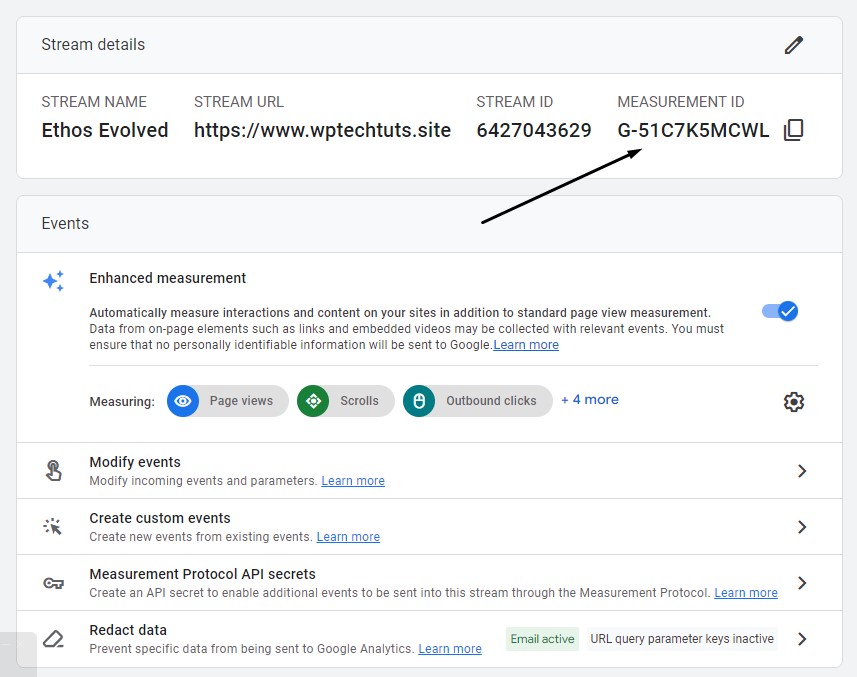
Copy that code and head back to Google Tag Manager. From the GTM dashboard, click on Add a new tag:
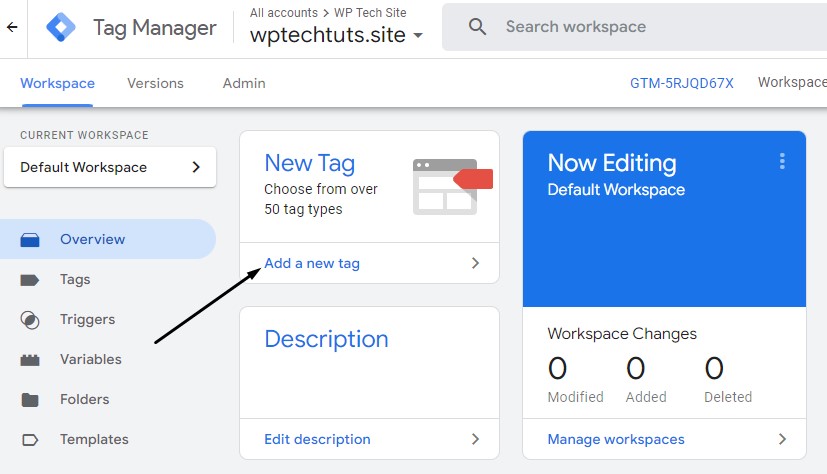
Then click on Tag Configuration, then Google Tag:
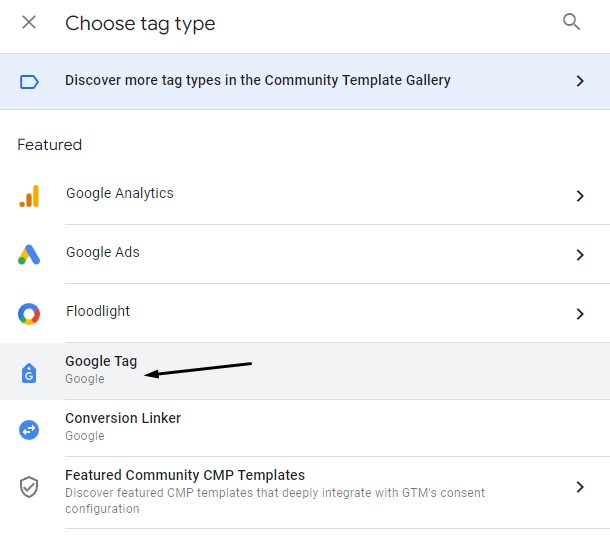
Paste your measurement ID into the Tag ID field:
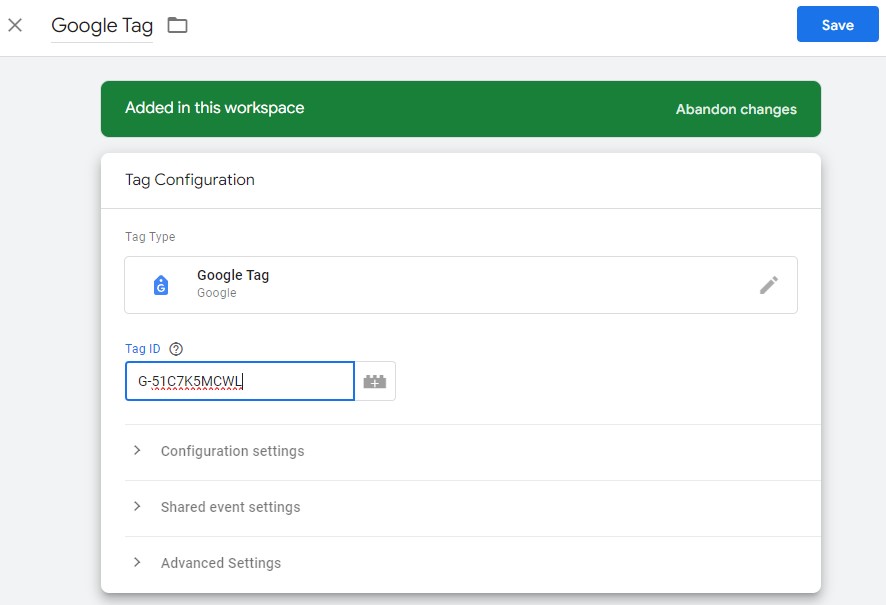
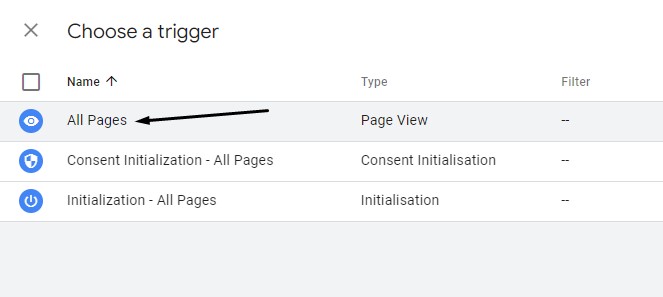
Then click on the Triggering box and choose All Pages:
Give your tag a title and click on Save:
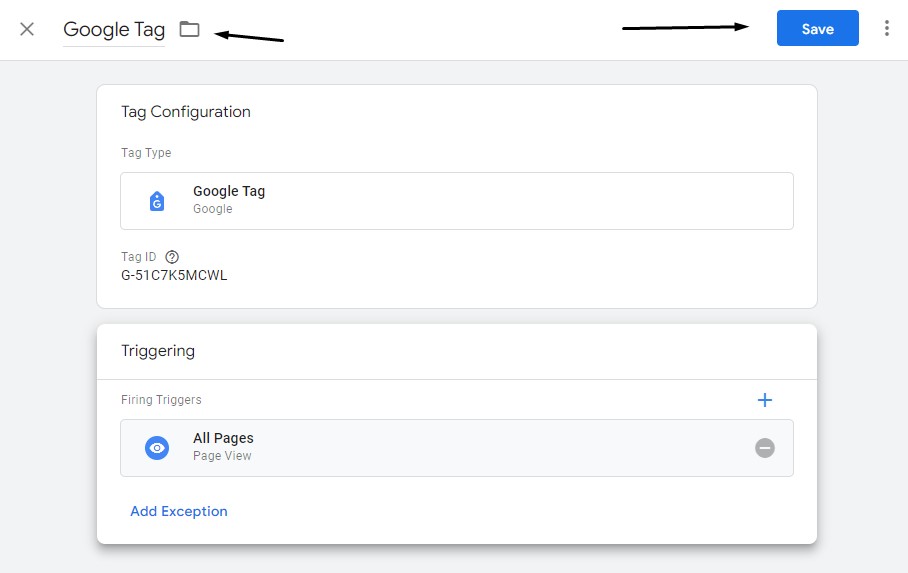
Now that you’ve added the Google Analytics Tag, you might want to test it’s working by clicking Preview again.
Type your domain name and wait for the popup to say it’s connected.
All that’s left to do is save this configuration by clicking on the Submit button:
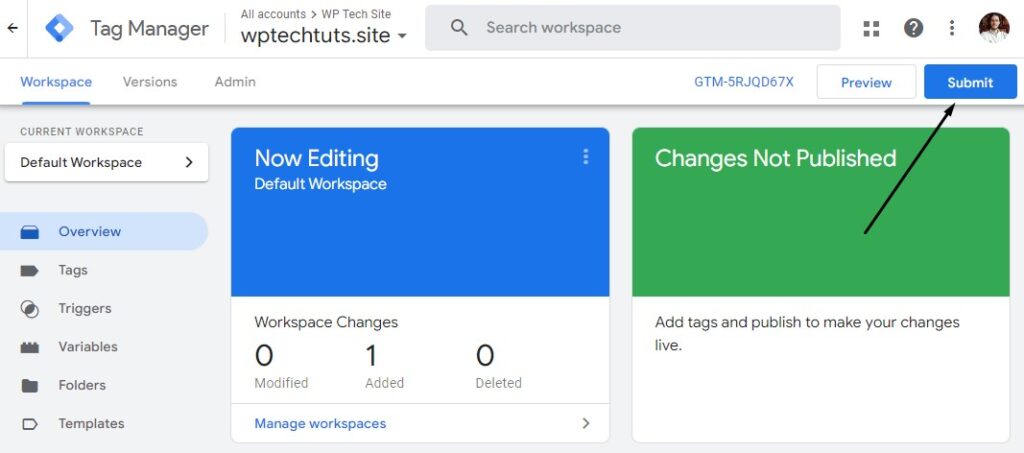
Name the configuration and click Publish:
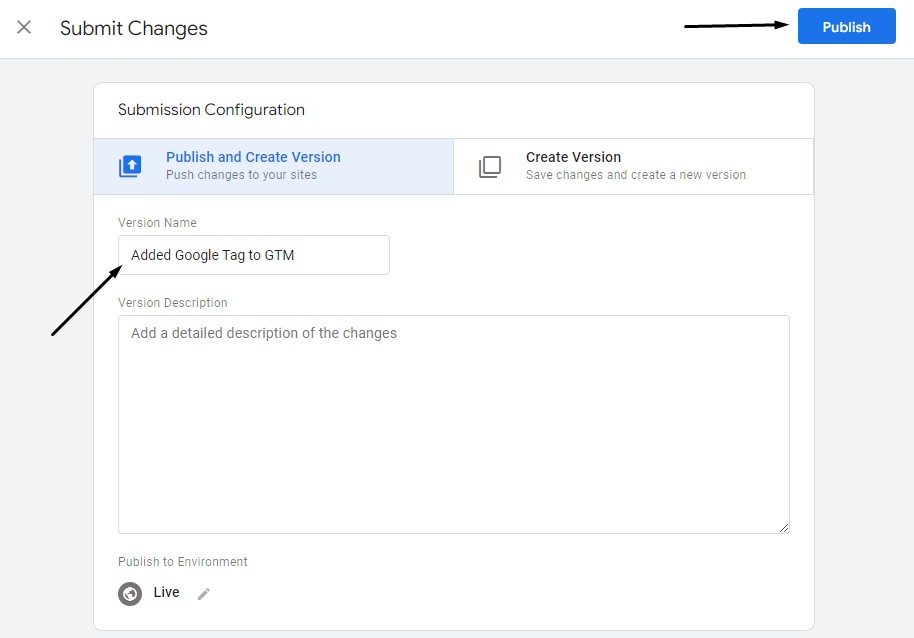
And that’s it! You’ve successfully added Google Analytics using Google Tag Manager.
The last thing to mention is that it’s important to remove any instances of the Google Analytics tracking code to your website if you’ve added it previously. This can be done after a few days of installing Tag Manager so that there aren’t any gaps in your GA reporting.
Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics – Conclusion
Hopefully, this post clarified the key differences between Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics.
Essentially, they are completely different tools that you can use together for more accurate and granular metrics inside Google Analytics.
Collecting GA data by installing GTM provides other benefits, such as website performance improvements and a simplified, user-friendly interface.
Now, if you want to discover more advanced GA4 and GTM tips, you can read our post on the best Google Analytics blogs.





